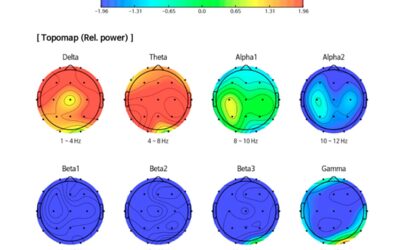
QEEG, or Quantitative Electroencephalography, is a software processing technique that uses statistical algorithms to identify salient features of the resting state EEG. Some platforms (WinEEG, EEGLab) also have the ability to separate salient features from background artifacts, which simplifies the interpretation of EEG data. The accuracy of qEEG processing is dependent upon the experience of the individual who is “reading” the resting state EEG and the degree of facility they have with the QEEG processing platform. In other words, there is a learning curve to acquiring the necessary skills to produce reliable results.
QEEG, or Quantitative Electroencephalography, is a higher-order statistical process that is used to condense a tremendous amount of information derived from brain signals into interpretable graphs, topographical headmaps and 3-dimensional brain illustrations with multiple voxels. The data output can be interpreted with respect to the patient’s presenting symptoms and may be used to confirm or rule-out neurological diagnoses, neuropsychiatric symptoms, and disorders related to cognitive, emotional, and behavioral symptoms. But the qEEG findings must always be vetted with a visual analysis of the resting state EEG.
Understanding qEEG Accuracy
Traditional EEG is the electrophysiological recording of brain activity using surface electrodes, whereas qEEG is the process by which statistical algorithms are applied to the EEG recordings to:
- Artifact out irrelevant electrical signals that are invariably included in the brain wave recordings that do not represent electrocortical activity (physiological and environmental artifacts like eyeblink, muscle, 60 HZ, etc).
- Produce graphs and Neuroimaging Brain Maps that show the distribution of EEG features like amplitude, power and frequency across the surface of the cortex.
- Compare the patient’s EEG results with age- and sometimes sex-matched normative controls.
Research on qEEG Accuracy
QEEG research has a long history in scholarly and academic research. Dr. John Hughes (1999) and Dr. E. Roy John (2006), the “Father of Neurometrics,” published extensively about the value of qEEG in psychiatry with respect to behavioral disorders, pharmacological interventions, and the development of normative databases for comparing a patient’s EEG/qEEG findings to normative controls. The application of qEEG analysis to mental health disorders shows more than 12 million Google citations as of May, 2024.
Interpreting QEEG Results
The accuracy of qEEG analysis is dependent on the skills of the user. A competent, well-trained electroencephalographer who uses qEEG analysis for clinical purposes in the mental health field will be able to design Neurofeedback brain-training protocols using qEEG results to treat a variety of presenting problems, like ADHD, sleep disorders, affective (mood) disorders, Autistic spectrum disorder (ASD), Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) and stroke, and many other categories of brain disorders. The interpretation of all qEEG results will depend on the clinician’s ability to read the resting state EEG because EEG analysis is a prerequisite for vetting the quality of qEEG results, especially those that are procured using AI.
Licensed mental health clinicians, health-care professionals from other career categories (MDs, chiropractors, nurses, etc), and researchers are encouraged to become Board Certified with the International qEEG Certification Board to elevate their practices to the highest standards when using qEEG processing and interpretation in their clinics and research settings.
In summary, in the hands of a licensed, qualified, well-trained and certified professional, EEG and qEEG analysis can be an enormous asset to any clinical practice in which the brain is viewed as the organ that is producing the problem.
References
[1] Hughes JR, John ER. Conventional and quantitative electroencephalography in psychiatry. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1999 Spring;11(2):190-208. doi: 10.1176/jnp.11.2.190. PMID: 10333991.
[2] John ER, Prichep LS. The relevance of QEEG to the evaluation of behavioral disorders and pharmacological interventions. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2006 Apr;37(2):135-43. doi: 10.1177/155005940603700210. PMID: 16733944.
[3] Kopańska M, Ochojska D, Dejnowicz-Velitchkov A, Banaś-Ząbczyk A. Quantitative Electroencephalography (QEEG) as an Innovative Diagnostic Tool in Mental Disorders. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 21;19(4):2465. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19042465. PMID: 35206651; PMCID: PMC8879113.
[3] seermedical.com: Briefly mention the blog’s perspective on qEEG accuracy (be objective).
[4] Yao Shun , Zhu Jieying , Li Shuiyan , Zhang Ruibin , Zhao Jiubo , Yang Xueling , Wang You. Bibliometric Analysis of Quantitative Electroencephalogram Research in Neuropsychiatric Disorders From 2000 to 2021. Frontiers in Psychiatry. (13) 2022.URL=https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychiatry/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.830819 DOI=10.3389/fpsyt.2022.830819
[5] https://www.bitbrain.com/blog/qeeg-brain-mapping[6] Frangopoulou, Maria Semeli, and Maryam Alimardani. 2022. “qEEG Analysis in the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Comparison of Functional Connectivity and Spectral Analysis” Applied Sciences 12, no. 10: 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105162