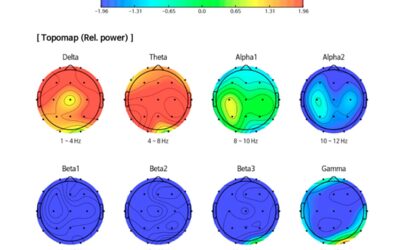
qEEG can help identify brain wave patterns associated with a variety of conditions, including:
- ADHD
- Depression
- Dementia
- Epilepsy
- Anxiety
- Panic disorder
- Autistic Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- TBI
- PTSD
- Schizophrenia
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Quantitative Electroencephalography (qEEG) offers a glimpse into the world of brainwaves, providing valuable insights into how our brains function. This technology goes beyond a simple EEG (Electroencephalography) by inquiring deeper into the electrical activity recorded from the scalp. qEEG analyzes this data using advanced algorithms, painting a detailed picture of brainwave patterns and their distribution across various regions.
But what exactly can qEEG detect?
- Identifying patterns associated with various conditions: qEEG findings can support the diagnosis of certain neurological and mental health conditions and track the progress of interventions using medications, neurological treatments and bra-training with Neurofeedback.
- Understanding brain function: By analyzing brainwave activity, qEEG can offer valuable information about attention, focus, emotional regulation, and cognitive processing.
- Informing treatment approaches: In some cases, qEEG data can be used to tailor interventions like neurofeedback therapy, potentially aiding in managing certain conditions.
It’s important to clarify that qEEG cannot definitively diagnose any medical condition. However, it can reveal patterns in brainwave activity that may be associated with certain conditions. Here’s a list of some conditions where qEEG findings can be supportive in the diagnostic process:
Neurological conditions:
- Mild Cognitive Impairment: qEEG can help to identify the normal aging process of the brain called “mild cognitive impairment” which impacts executive functioning.
- Dementia: qEEG can help differentiate between various types of dementia like Alzheimer’s vs Vascular dementia.
- Epilepsy: EEG, the foundation of qEEG, plays a crucial role in identifying abnormal brain activity patterns associated with seizures.
Mental health conditions:
- ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder): qEEG may reveal specific brainwave patterns potentially linked to inattentiveness or hyperactivity symptoms in ADHD.
- Anxiety and Depression: While not diagnostic, qEEG findings can sometimes show alterations in brainwave activity that correlate with these conditions.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): qEEG may identify patterns in brainwave activity that align with symptoms commonly observed in ASD, such as difficulties with social interaction and communication.
QEEG: A Tool to detect Symptoms Associated with Autism, ADHD and Dementia
Can you see autism on a QEEG?
Although the technical aspects of functional localization of autism (ASD) are too lengthy to explain here, qEEG analysis can reveal a profile of symptoms that are congruent with an ASD diagnosis.
These symptoms include difficulty with reading and math comprehension, problems with mirroring or vicarious learning, poor attention to the outside world, poor self-regulation skills, anxiety, and poor social prosody function (making eye-contact, interpreting body language, tone of voice or other social-affective nuances in communication with others).
Can qEEG detect ADHD?
ADHD is a psychological diagnosis involving issues with executive function that is normally assessed by a psychiatrist, a psychologist, a pediatrician or family doctor, a nurse practitioner, a master level counselor, or a social worker.
Regardless of the professional occupation of the qEEG practitioner, those who are competent and experienced in qEEG assessment and Neurofeedback training generally agree that symptoms of Type I (Inattentive type) or Type II (Hyperactive type) ADHD have EEG brain mapping correlates that may be successfully addressed with neurofeedback.
One complication of accurate qEEG determination of ADHD is if the individual also has chronic sleep quality issues. The effects of poor sleep quality on attention, focus and hyperactivity are almost identical to those of ADHD.
Indeed, for individuals who do not have a diagnosis of ADHD, chronic insufficient restorative sleep quality will produce executive function symptoms of inattentiveness, problems with focus and even hyperactivity.
Although the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) advises against the use of qEEG to either diagnose or confirm an ADHD diagnosis made by a clinician based on DSM-V criteria, neurologists are not generally the type of specialist that an individual would consult if ADHD were suspected.
Neurologists are specialists who are trained in managing the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders, which are disorders of the nervous system (i.e., brain, spinal cord, and nerves). They also tend to focus on Neuroimaging of the central nervous system using MRI, CT Scans, PET scans and SPECT Scans, all anatomical indicators, rather than Functional NeuroImaging, which gives the EEg/qEEG provider an analysis of the real-time function of the brain. Hence, neurologists are better equipped to treat and diagnose neurological disorders like epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.
The AAN weighs-in on this issue based on the belief that only medical professionals should use QEEG, an opinion that is not shared by the majority of competent and responsible EEG and qEEG practitioners. This article offers you a longer reading on the discussion.
Can brain mapping detect dementia?
Yes, there is abundant scholarly research supporting clinical applications for the detection of dementia as well as the differentiation between different types of dementia using EEG/qEEG criteria.
As of January 2024, 159,000 scholarly papers on qEEG and dementia were listed on Google. Quantitative EEG (qEEG) analysis provides information on physiologically meaningful metrics of resting state EEG status to differentiate states of mild cognitive impairment and different stages of Alzheimer’s Dementia.
Non-medical qEEG practitioners can use these biomarker components to justify a referral to a neurologist for future clinical work-up.
References
Smailovic, U., Jelic, V. Neurophysiological Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease: Quantitative EEG Approach. Neurol Ther 8 (Suppl 2), 37–55 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40120-019-00169-0
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40120-019-00169-0#citeas
Livinț Popa L, Dragoș HM, Strilciuc Ș, Pantelemon C, Mureșanu I, Dina C, Văcăraș V, Mureșanu D. Added Value of QEEG for the Differential Diagnosis of Common Forms of Dementia. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2021 May;52(3):201-210. doi: 10.1177/1550059420971122. Epub 2020 Nov 8. PMID: 33166175. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33166175/
Thompson L, Thompson M, Reid A. Functional neuroanatomy, and the rationale for using EEG biofeedback for clients with Asperger’s syndrome. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2010 Mar;35(1):39-61. doi: 10.1007/s10484-009-9095-0. Epub 2009 Jul 1. PMID: 19568927. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19568927/
Thompson L, Thompson M, Reid A. Neurofeedback outcomes in clients with Asperger’s syndrome. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2010 Mar;35(1):63-81. doi: 10.1007/s10484-009-9120-3. PMID: 19908142. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19908142/