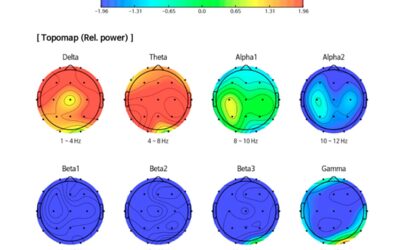
A qEEG, or Quantitative Electroencephalography, is a powerful tool used to analyze brain activity by recording and measuring electrical signals emitted by neurons in the brain.
19 sensors are placed on the surface of the head and brain wave activity is recorded over those 19 areas. By capturing these signals and processing them through specialized software, qEEG generates detailed maps and graphs that provide insights into brain function and abnormalities.
Table of Contents
- Here’s how qEEG works
- What is the difference between EEG and qEEG?
- What are the risks of brain mapping?
- Is qEEG legit?
- Is qEEG FDA approved?
- Is qEEG mapping a type of neurofeedback training?
- References
Here’s how qEEG works
- Electroencephalography (EEG): This initial step measures the electrical activity of your brain using electrodes placed on your scalp. These readings represent brainwaves, reflecting the communication between neurons.
- Quantitative Analysis: This is where qEEG comes in. The digitized EEG data is fed into computers and analyzed using advanced algorithms.
- Brain Mapping: Through this analysis, qEEG creates a visual representation of brain activity, often referred to as a “brain map.” This map displays the strength and distribution of brain waves across different regions.
Think of a brain map as a topographical landscape
- Different colors represent varying levels of brainwave activity.
- By comparing this map to a normative database (representing “average” brainwave patterns), experts can identify potential areas of concern.
Key Points about QEEG
- Non-invasive and painless: Similar to measuring cardiac activity with an ECG,, QEEG simply records brain activity without affecting it.
- Clinical Tool: Trained professionals can use QEEG information to assess brain function, track changes due to interventions like neurofeedback or medication, and potentially aid in diagnosis.
- Advanced Techniques: Emerging methods like Independent Component Analysis (ICA) can further pinpoint the source of brain activity, enhancing our understanding of brain function.
Summarizing, QEEG acts as a powerful lens, offering a detailed view of brain function. This information can be valuable for certified healthcare professionals in guiding treatment plans and understanding the brain’s response to interventions.
What is the difference between EEG and qEEG?
EEG (Electroencephalography)
- Basic Measurement:
- Records electrical activity of the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp.
- Similar to measuring cardiac activity with an ECG.
- Output:
- Provides a raw representation of brainwave patterns over time.
- Visualized as a series of lines on a graph.
- Analysis:
- Primarily relies on visual interpretation by trained professionals.
- Limited ability to pinpoint specific brain regions or subtle abnormalities.
qEEG (Quantitative Electroencephalography)
- Advanced Analysis:
- Analyzes the digitized EEG data using sophisticated algorithms and computer software.
- Detailed Insights:
- Extracts numerous features from the raw EEG signal, including:
- Frequency: Measures the speed of brainwaves (e.g., theta, alpha, beta).
- Amplitude: Indicates the strength of brainwave activity.
- Location: Provides a topographical map of brain activity across different regions.
- Extracts numerous features from the raw EEG signal, including:
- Visual Representation:
- Creates “brain maps” – color-coded visualizations highlighting the distribution and strength of brainwaves in various brain areas.
- Clinical Applications:
- Offers a more objective and quantitative assessment of brain function compared to visual EEG analysis.
- Can be used to:
- Identify potential abnormalities in brainwave patterns.
- Track changes in brain function over time (e.g., during neurofeedback therapy) or in response to medications.
- Potentially aid in diagnosis when used in conjunction with other clinical assessments.
Key Differences between EEG and qEEG
- Complexity: EEG is a simpler measurement, while qEEG involves in-depth analysis using advanced software.
- Information Output: EEG provides a basic picture, while qEEG offers a more comprehensive and quantitative analysis.
- Clinical Utility: qEEG offers greater potential for clinical applications due to its detailed information and ability to pinpoint specific brain regions.
In essence
- EEG is like a basic snapshot of brain activity.
- qEEG is a detailed analysis, similar to examining a high-resolution image.
What are the risks of brain mapping?
Brain mapping is a noninvasive and painless procedure, unlike SPECT or PET scans. Similar to how an ECG measures cardiac electrical activity without altering it, brain mapping records the brain’s electrical activity for analysis without impacting the brain itself. The recorded brain activity is then compared to an FDA-approved normative database to detect any abnormal areas, which assists in identifying specific areas needing attention during neurofeedback treatment.
Is qEEG legit?
Electroencephalography (EEG) itself is a well-established method for recording and analyzing brain activity. Quantitative EEG (qEEG) is a computational methodology that condenses extensive data about EEG brain activity into easily interpretable maps or graphs. This process facilitates a comprehensive analysis of the brain’s functioning, aiding in diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Quantitative EEG (qEEG) stands on solid scientific grounds supported by extensive research and practical applications. Its ability to decipher complex brain activity patterns opens doors to innovative diagnostic and therapeutic interventions. Both EEG and qEEG are supported by professional organizations that encourage EEG/qEEG research and applied clinical applications. Three of the most well known and respected organizations are:
- AAPB – Association of Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback
- ISNR – International Society of Neuroregulation and Research
- IQEEGCB – International qEEG Certification Board
Moreover, it’s noteworthy that qEEG is not an isolated practice but rather an integral part of various professional fields. From psychology to medicine, nursing to education, qEEG finds applications across a spectrum of healthcare domains. Professional organizations dedicated to EEG and qEEG research actively support the advancement of these methodologies. They foster a community of professionals through memberships, publications, and international conferences, further validating the legitimacy and relevance of qEEG in contemporary healthcare practices
One of the most compelling aspects of qEEG is its ability to compare an individual’s brain activity to that of a “normal” population. By identifying deviations from the norm, qEEG provides valuable insights into potential neurological conditions or cognitive, emotional, or behavioral patterns. This comparative analysis enhances diagnostic accuracy and informs targeted treatment strategies.
In conclusion, if you’ve ever questioned the legitimacy of qEEG, rest assured that it is a legitimate and valuable tool in the realm of neuroscience and healthcare when used in the hands of knowledgeable professionals.. Its contributions extend beyond diagnosis, influencing treatment approaches and enhancing our understanding of the intricate workings of the human brain.
Is qEEG FDA approved?
Several qEEG products have successfully obtained Class 2 FDA medical device clearance, signifying that they have met the FDA’s requirements for safety and effectiveness. This clearance indicates that these products can be marketed and used for medical purposes with proper regulatory oversight.
QEEG software that has been developed for clinical and research purposes to examine the brain requires FDA approval if it is included in an EEG amplifier operating system that is marketed to the public for medical purposes.
For qEEG software to be FDA approved, it typically needs to demonstrate its safety and effectiveness through clinical trials and rigorous testing. This process ensures that healthcare providers and patients can rely on the accuracy and reliability of the software’s results when making diagnostic and treatment decisions.
It’s important to note that while some qEEG software may require FDA approval for medical use, there are also open-source toolboxes available, such as EEGLAB or the Neurophysiological Biomarker Toolbox, which allow researchers and clinicians to perform qEEG analysis. While these open-source tools may not undergo the same FDA approval process as commercial products, they still provide valuable resources for studying brain activity and advancing our understanding of neurological conditions.
In conclusion, qEEG software developed for clinical and research purposes must undergo FDA approval if intended for use in medical settings. This regulatory process ensures the safety and effectiveness of the software, providing healthcare providers with reliable tools for assessing and managing neurological conditions like epilepsy.
Is qEEG mapping a type of neurofeedback training?

No, qEEG mapping, or “brain mapping” is not a type of neurofeedback training but is used as an assessment tool to analyze the complexity of brain function. “qEEG-guided neurofeedback training” is defined as the use of qEEG data to develop effective neurofeedback training protocols to optimize brain function.
qEEG mapping, commonly known as “brain mapping,” serves as an assessment tool rather than a form of neurofeedback training. While both techniques involve recording brain activity, their purposes and methodologies differ significantly.
Neurofeedback training entails providing real-time feedback to individuals about their brainwave patterns, allowing them to learn to regulate these patterns for improved cognitive function or symptom relief. In contrast, qEEG mapping involves the collection and analysis of EEG data to create a comprehensive map of brain activity patterns, providing valuable insights into brain function and potential abnormalities.
The distinction lies in their respective roles within the realm of neuroscience. qEEG mapping serves as a diagnostic tool, helping clinicians identify specific areas of dysfunction or deviation from normal brain activity. This information then informs the development of targeted interventions, such as neurofeedback training protocols, tailored to address the individual’s unique brain patterns and needs.
Furthermore, qEEG-guided neurofeedback training utilizes the insights gained from qEEG mapping to customize neurofeedback protocols for optimal effectiveness. By incorporating individualized data from qEEG assessments, clinicians can create targeted neurofeedback interventions designed to address specific cognitive or behavioral challenges.
In summary, while qEEG mapping and neurofeedback training both involve the analysis of brain activity, they serve distinct purposes within the field of neuroscience. qEEG mapping functions as an assessment tool to analyze brain function and inform treatment planning, while neurofeedback training involves using real-time feedback to help individuals learn to self-regulate their brainwave patterns. Together, these techniques offer valuable insights and interventions for optimizing brain function and enhancing overall well-being.
References
Hoffman, D.A., Lubar, J., Thatcher, R.W., Sterman, M.B., Rosenfeld, P.J., Striefel, S., Trudeau, S., Stockdale, S. Limitations of the American Academy of Neurology and American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Paper on qEEG, J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 11:3, Summer 1999.
Kanda PAM, Anghinah R, Smidth MT, Silva JM. The clinical use of quantitative EEG in cognitive disorders. Dement Neuropsychol. 2009 Jul-Sep;3(3):195-203. doi: 10.1590/S1980-57642009DN30300004. PMID: 29213628; PMCID: PMC5618973
Livint Popa L, Dragos H, Pantelemon C, Verisezan Rosu O, Strilciuc S. The Role of Quantitative EEG in the Diagnosis of Neuropsychiatric Disorders. J Med Life. 2020 Jan-Mar;13(1):8-15. doi: 10.25122/jml-2019-0085. PMID: 32341694; PMCID: PMC7175442.
Nuwer M: Assessment of digital EEG, quantitative EEG and EEG brain mapping: report of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Clinical Neurophysiology Society. Neurology 1997; 49:277–292
Prichep, L.S., John, E.R. qEEG profiles in psychiatric disorders. Brain Topography, 4:4, 1992.
qEEG Support: What is qEEG/Brain Mapping? https://qEEGsupport.com/what-is-qEEG-or-brain-mapping/
Thatcher, Robert. (2010). Validity and Reliability of Quantitative Electroencephalography. Journal of Neurotherapy. 14. 122-152. 10.1080/10874201003773500.